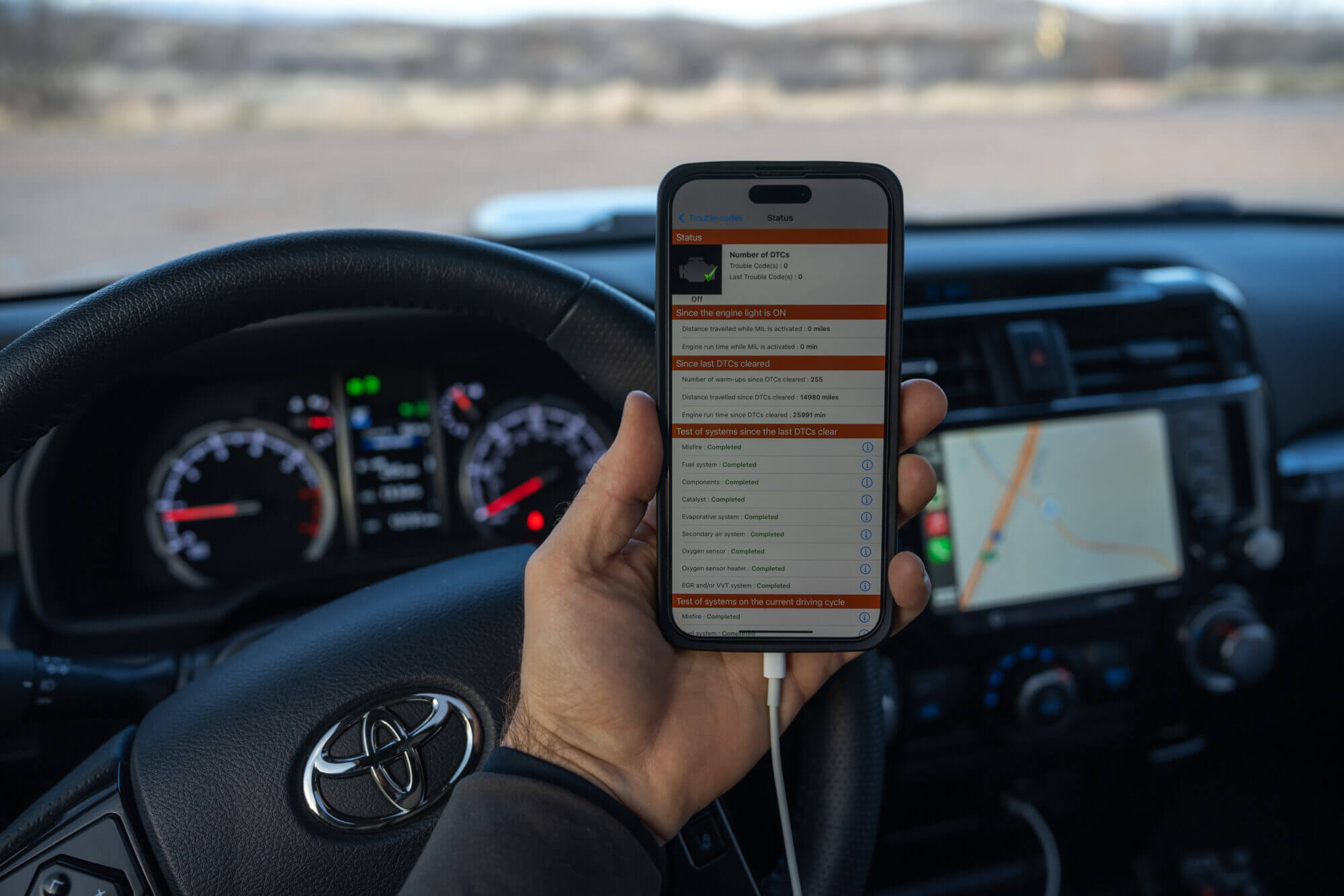

A Check Engine Light or another warning indicator can pop on the dash, no matter how old or new your truck or SUV might be. You could take it to the dealership and get it checked out, but if you’re busy on the trails or an avid DIYer, it’s easier to just check the codes yourself. If you have a relatively new off-roader equipped with an OBD II port, diagnosing a potential issue is really easy and straightforward provided you have a code reader.

What are OBD-II Codes?
OBD-II codes are used to detect issues with the vehicle, whether they’re mechanical or electrical in nature, and subsequently diagnose the specific problem in order to fix it. OBD codes are divided into four different segments, depending on which letter the code starts with. If it stats with ‘P’, it means there’s an issue with the powertrain system. ‘B’ stands for body, ‘C’ stands for chassis, while ‘U’ means there’s something wrong with the network and wiring system.

How are OBD-II Codes Used?
Having a way to diagnose OBD II faults and codes is essential in this day and age, where most vehicles are equipped with smart ECUs and usually dozens if not hundreds of different sensors and electronics. Nowadays, you can even buy an OBD II splitter or pass through a harness that will allow you to connect other OBD-II devices while still maintaining use of your original OBD port.
That being said, being able to read fault codes and actually understand them are two different things altogether. This article will help you understand some of the more common fault codes and explain what they mean. This can come in handy especially if you’ve gotten stuck while off-roading out in the middle of nowhere.
Most Common Codes & When to Use Them
P0300-P0305
The first code is arguably the most common one: P0300. This code stands for a random or multiple cylinder misfire. Although it can crop up on its own, this code is usually accompanied by several other codes, typically codes P0301 through P0308. If you get a P0301 fault code, it would imply that the first cylinder is experiencing misfire, P0302 would mean that your second cylinder is misfiring, and so on.
Common symptoms indicating that you might have issues with a cylinder misfire include but are not limited to rough idle, a check engine light, sluggish acceleration, and weird exhaust sounds (the engine will sound like it’s choppy or skipping a beat).
P0171 to P0175
Much like P0300, these fault codes are really common. If you notice a fault code between P0171 and P0175, it means that your engine is running lean; the fuel-air mixture is oversaturated with air.
As you might expect, common symptoms include an engine that’s running extremely rough and is hesitant to idle consistently as well as underwhelming performance and delayed power delivery. Your vehicle will feel like it lost most of its horsepower and is really lazy to rev. Although a number of issues could cause your engine to run lean, it all boils down to not having enough fuel or having too much air entering the cylinder chambers.
A bad fuel pump could be starving your engine of fuel causing it to run lean, but you might also have a bad mass airflow sensor sending way too much air into the engine. Likewise, the issue could be something as simple as a disconnected vacuum hose. Fixing this fault code is harder since you’ll need to diagnose the individual component causing the issue, but at least these OBD II fault codes will help you narrow it down and track it more easily.
P0420, P0430
Both of these codes indicate that there’s an issue with your catalytic converter, and more specifically, they signal low catalyst system efficiency.
The catalytic converter is an important part of your vehicle’s exhaust system. It’s responsible for converting certain pollutants coming out of your combustion chamber and filtering them before they’re expelled into the environment via the exhaust system. The catalytic converter essentially burns up hydrocarbons before they exit the exhaust system, thus reducing environment pollution.
A bad or broken catalytic converter might cause your vehicle to exude a weird smell but you’ll probably notice decreased fuel economy before you notice anything else.
Decreased engine performance can also happen because of a bad catalytic converter, but it’s relatively rare.
In any case, if you get a P0420 or a P0430 code you might want to get your exhaust system checked out and, more specifically, the catalytic converter. P0420 simply means there’s an issue with cylinder bank 1, and P0430 means there’s an issue with the converter on cylinder bank 2.

P0141
This fault code indicates that there’s something wrong with the O2 sensor heater circuit. It essentially signals a malfunction with the O2 bank 1 sensor 2 heater circuit. This is the sensor behind the catalyst on cylinder bank 1.
On each startup, the vehicle’s ECU tests the O2 sensor and if it detects there’s anything wrong with it, it’ll throw up this notorious P0141 fault code.
Symptoms indicating that there’s something wrong with the O2 sensor include a check engine light on the dash, worse fuel economy than usual, and even misfires on extremely rare occasions. That being said, this fault code is only moderately serious meaning you can still drive your car but you should get it checked out as soon as you can.
P0446, P0455
These codes aren’t as common as the ones listed above, but you might still see them every now and then. If you see P0455, there’s probably a major leak in your vehicle’s Evaporative Emission Control System. This just means that your fueling system isn’t sealing properly and it can’t create a full vacuum (there’s air escaping from somewhere).
Before you do anything else, check the gas cap and see whether the seal around it is cracked or otherwise damaged. Other common issues include a disconnected EVAP hose or a purge valve that’s stuck permanently open. Common symptoms include a Check Engine Light and a light whiff of gasoline smell emanating from the tank area.
Similarly, P0446 just indicates that there’s probably an issue with the shut-off valve as opposed to just a general leak in the EVAP system that P0455 indicates. In essence, P0446 is a much more specific fault code that narrows down the problem and leaves you with less guess work.
P0299
This fault code means that your ECU has detected a turbocharger or a supercharger underboost condition. In essence, it just means that your turbo or supercharger isn’t delivering full power to the engine because of one issue or another, and so, you might experience reduced performance, poor throttle response, increased fuel consumption, as well as a check engine light.
This is considered a generic code and not critical in any way, but you should still check it out as soon as you can as opposed to delaying fixing it for weeks or even months on end.
These are some of the more common OBD II fault codes, but there are hundreds more that you’ll hopefully never need to know. If you need to pick up your own code reader or parts to fix a Check Engine Light, look no further than 4 Wheel Parts!



2